OS Development on MacOS
Most users can simply use a pre-built binary from the releases page and install it manually or using the web installer.
But if you want to modify things under the hood, you're in the right place!
Get the prerequisites
Make sure you have everything installed to compile code:
xcode-select --install
brew install pkg-config libffi ninja make SDL2
Download the code
Clone the repositories:
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/MicroPythonOS/MicroPythonOS.git
cd MicroPythonOS/
That will take a while, because it recursively clones MicroPython, LVGL, ESP-IDF and all their dependencies.
Optional: updating the code
If you already have an old clone and you want to update it, the easiest is to just delete it and re-clone.
But if you need to save on bandwidth and time, you can instead do the following, which will throw away all local modifications:
cd MicroPythonOS/
git submodule foreach --recursive 'git clean -f; git checkout .'
git pull --recurse-submodules
Compile the code
Use the build_mpos.sh script for convenience.
Usage:
./scripts/build_mpos.sh <target system>
Target systems: esp32, esp32s3, unix (= Linux) and macOS
Examples:
./scripts/build_mpos.sh esp32
./scripts/build_mpos.sh esp32s3
./scripts/build_mpos.sh unix
./scripts/build_mpos.sh macOS
The resulting build file will be in lvgl_micropython/build/, for example:
lvgl_micropython/build/lvgl_micropy_unixlvgl_micropython/build/lvgl_micropy_macOSlvgl_micropython/build/lvgl_micropy_ESP32_GENERIC_S3-SPIRAM_OCT-16.bin
Running on desktop
-
Make sure you have the
internal_filesystem/folderIf you built from source, you will already have a local clone that contains it.
If you used a pre-built binary, then you need to get a local clone and change into that directory with:
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/MicroPythonOS/MicroPythonOS.git cd MicroPythonOS/ -
Make sure you have the software
The easiest is to downloaded a pre-built binary (like
MicroPythonOS_amd64_macOS_0.7.1.binorMicroPythonOS_amd64_linux_0.7.1.elf) from the releases page.After downloading it, put it in the right location like this:
mkdir -p lvgl_micropython/build # do this from within in the folder MicroPythonOS/ you cloned in step 1 cp /Users/yourname/MicroPythonOS_amd64_macOS_0.7.1.bin lvgl_micropython/build/lvgl_micropy_macOS # for macOS cp /home/yourname/MicroPythonOS_amd64_linux_0.7.1.elf lvgl_micropython/build/lvgl_micropy_unix # for Linux or WSL2 on Windows 11Alternatively, instead of downloading a pre-built binary, you can build it from source, and then you will have the built binary in
lvgl_micropython/build/lvgl_micropy_XXXwhere XXX is unix or macOS. -
Start the software:
You're now ready to run it with:
./scripts/run_desktop.sh
Notes on MacOS
If you get an error about a missing /opt/homebrew/opt/libffi/lib/libffi.8.dylib then fix that with: brew install libffi
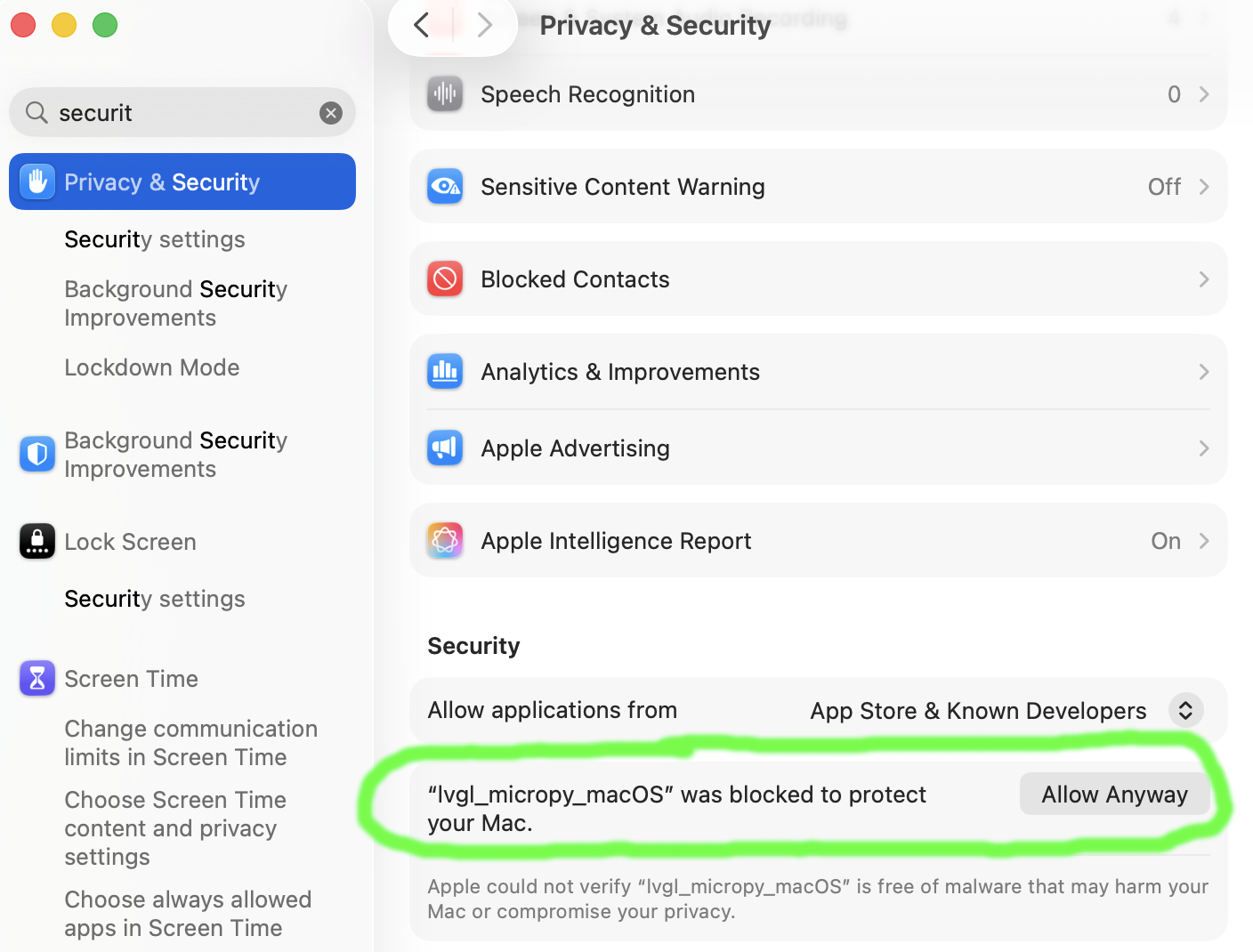
If you get an error about the code being unsigned, then allow it like this:
Making Changes on Desktop
You'll notice that whenever you change a file in internal_filesystem/, the changes are immediately visible on desktop when you reload the file or restart the app.
When you run ./scripts/run_desktop.sh, the OS runs the MicroPythonOS scripts directly from internal_filesystem/. This means:
- All changes to Python files are immediately active - no build or install needed
- Instant testing - edit a file, restart the app, see the changes
- Fast iteration cycle - the recommended way to develop and test
Try it yourself:
- Edit
internal_filesystem/builtin/apps/com.micropythonos.about/assets/about.py - Run
./scripts/run_desktop.sh - Open the About app
- See your changes immediately!
Making Changes on ESP32
Once you've tested your changes on desktop and they work correctly, or you're doing things you can't test on desktop, then you can deploy to physical hardware.
The easiest way to install on the ESP32 is using the webinstaller, of course.
But if you need to install a version that's not available there, or you built your own, then you can manually install it on an ESP32 device.
-
Get the firmware
-
Put the ESP32 in Bootloader Mode
If you're already in MicroPythonOS: go to Settings - Restart to Bootloader - Bootloader - Save.
Otherwise, physically keep the "BOOT" (sometimes labeled "START") button pressed while powering up the board. This is explained in more detail at the webinstaller
-
Flash the firmware
~/.espressif/python_env/idf5.2_py3.9_env/bin/python -m esptool --chip esp32s3 write_flash 0 firmware_file.binAdd the
--erase-alloption if you want to erase the entire flash memory, so that no old files or apps will remain.There's also a convenient
./scripts/flash_over_usb.shscript that will attempt to flash the latest firmware that you compiled yourself. -
Access the MicroPython REPL shell
After reset, the REPL shell should be available on the serial line.
Any serial client will do, but it's convenient to use the
mpremote.pytool that's shipped with lvgl_micropython:lvgl_micropython/lib/micropython/tools/mpremote/mpremote.py -
Populate the filesystem (only for development)
In development, you probably want to override the "frozen" libraries and apps that are compiled in, and replace them with source files, which you can edit.
This makes MicroPythonOS startup a lot slower, as the Python scripts have to be compiled at runtime instead of at build time. But once MicroPythonOS and the code you're testing has loaded, the speed will be normal again.
There's a convenient script that will do this for you.
Usage:
./scripts/install.sh./scripts/install.sh com.micropythonos.about # to install one single appOn MacOS, the install.sh script needs:
brew install --cask serialIf you need to frequently update a small number of files, you can also update them manually, for example:
mpremote.py cp internal_filesystem/lib/mpos/device_info.py :/lib/mpos
Notes
- Ensure your ESP32 is compatible (see Supported Hardware). If it's not, then you might need the Porting Guide.